If you’ve ever thought about how to become a cyber security specialist, I’m sure your first question was, “what’s a cyber security specialist?” Trust me, you’re not alone; this pic says it all!
The reality is that no one can give you an exact definition with 100% confidence. But I did my research, and maybe I can help shed some light on the role.
If that interests you, I’ll try to discuss all the things you need to know to become a cyber security specialist.
But before we dive in, let’s get one thing out of the way first.
IT Security Specialist vs Cyber Security Specialist
As you do your own research, understand that there’s no difference between an IT Security Specialist vs Cyber Security Specialist. You’ll also see variations of the title which don’t really make a major difference either:
- Information Security Specialist vs IT Security Specialist
- Cybersecurity Specialist vs Cyber Security Specialist
- Security Specialists
- Privacy Specialist
- Cyber Defense Infrastructure Support Specialist
- Cyber Security Operations Specialist
The list goes on, but the point is…they all mean nearly the same thing! To simply things for you, I’ll try to stick with the term, “cyber security specialist”.
Now if you’re ready, let’s dive in!
What Is a Cyber Security Specialist?
According to NICCS (National Initiative For Cybersecurity Careers And Studies), if you become a cyber security specialist, your main goal is the “ability to apply cybersecurity and privacy principles to organizational requirements (relevant to confidentiality, integrity, availability, authentication, non-repudiation).”
In other words, you’re the professional responsible for protecting your organization’s computer systems, networks, and data from security breaches or potential threats.
Key aspects of a cyber security specialist role include:
- Risk Assessment
- Security Measures Implementation
- Monitoring and Detection
- Incident Response
- Education and Training
- Compliance and Auditing
Just keep in mind that your role will vary based on the specific cyber security domain you’re in. For example, a GRC Specialist vs. Security Operations Specialist vs. Threat Intel Specialist, etc.
I’ll go more in-depth on the responsibilities later, so let’s get into what you really want to know.
Salary of Cyber Security Specialist?
Now, the most important discussion is…money! How much does a cyber security specialist make a year?
Security specialists play a crucial role in any IT department, so the entry-level salaries are quite decent.
I’m going to show you several different websites to give you an idea of what an entry level cyber security specialist can earn.
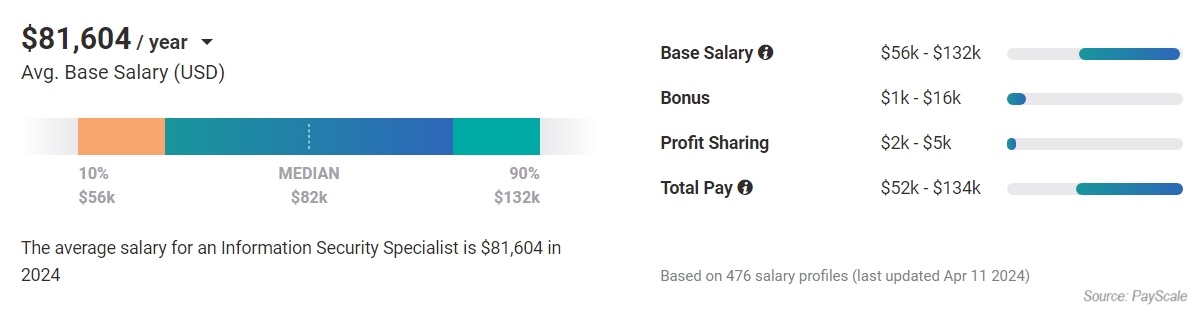
Here’s a look at what PayScale mentions (it doesn’t do a good job of showing an entry level salary, so I took the median value):
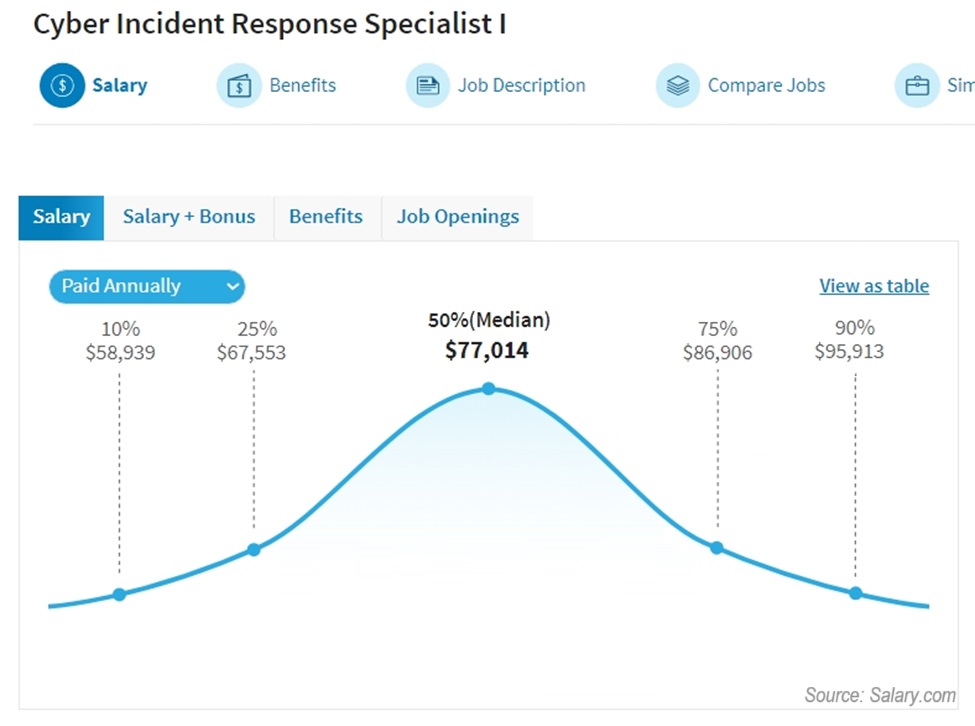
And since Salary.com didn’t have a cyber security specialist position, I found the closest thing with a median salary of $77,014:
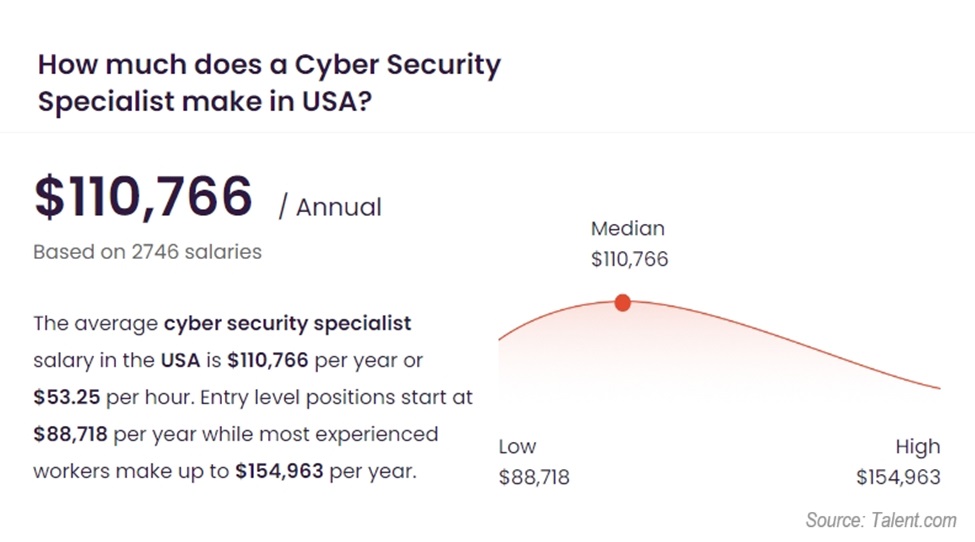
Talent.com displays a base salary of $88,718:
Finally, Glassdoor had several different titles for the same position, so I picked the most relevant. The important thing to note is the lower base pay of $88K:
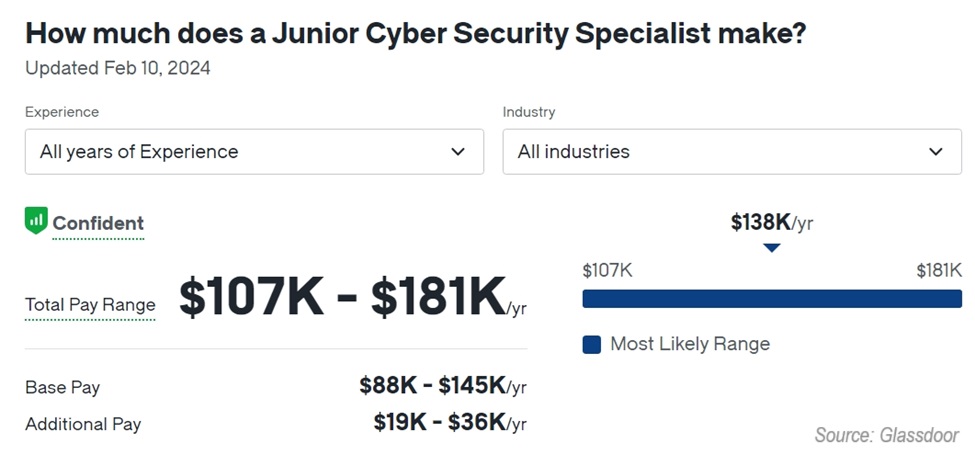
When I put it all together, that makes the average salary of a cyber security specialists in the US about $83,834 per year.
That’s really close to what Cyberseek found…am I good or am I good!
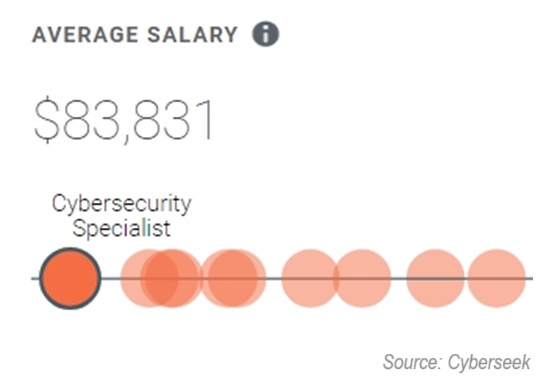
As you break it down, that brings the average cyber security specialist salary per month to roughly $6,986…not bad for starting out!
Of course, as you gain more experience, you’ll easily make it into the six-figure range.
But how much demand is there for this role?
What’s the Demand of a Cyber Security Specialist?
Aside from money, why else would you choose to become a cyber security specialist?
Well, job stability and demand are great reasons to pursue this career.
That’s because every company that utilizes technology will need your services at some point, either as an employee or consultant.
Cyberseek shows 8,200+ jobs are available to security specialists nationally.

It also showed that NICE (National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education) reported 56K+ job openings for “Cyber Defense Infrastructure Support Specialist.” Even after reading the image footnote, it still appears you have quite a bit of demand.
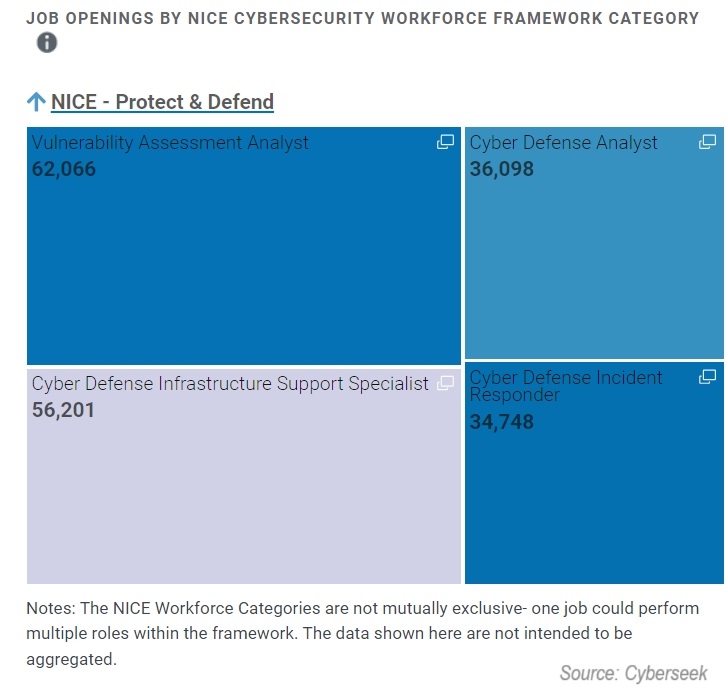
Ultimately, as a cyber security specialist your job is to apply cybersecurity and privacy principles to organizational requirements. That means your role is very technical and hands-on, hence the title, cyber security “specialist.”
Okay, let’s get into the duties of a cyber security specialist.
What Do Cyber Security Specialists Do?
Here are some of the more common responsibilities that cyber security specialists focus on (again your specific duties may differ):
- Threat Identification: Detecting potential threats and vulnerabilities in systems and network infrastructure. This involves staying up-to-date with the latest threats and security trends.
- Security Solutions Implementation: Installing and configuring software, such as firewalls, anti-virus solutions, and intrusion detection systems, to protect against unauthorized access and attacks.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitoring systems and network traffic for unusual activities that might indicate a security breach. Using tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) to gather and analyze data from various sources within the enterprise. Monitoring security upgrades and evaluating their ability to mitigate previously identified security vulnerabilities becomes crucial to understand if the organization’s security measures were successful.
- Incident Response: Acting quickly to contain and mitigate the effects of security breaches and attacks when they occur. This involves investigating the root cause and implementing recovery plans.
- Development and Implementation: Once deficiencies have been identified, you’ll aid in developing and possibly implementing strategies to mitigate security concerns while optimizing the IT infrastructure.
- Risk Assessments and Audits: Conducting regular assessments of the security posture of the organization. This includes performing vulnerability scans and penetration testing to identify weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- Policy and Compliance: Ensure your organization adheres to all applicable laws, regulations, and standards concerning cyber security. This might include developing and maintaining the organization’s security policies and procedures.
- Education and Training: Providing training and guidance to other employees on cyber security best practices and new security policies. This helps to foster a security-aware culture within the organization.
- Counseling: Because of your knowledge and experience, be prepared to spend a significant amount of time educating your employer regarding: security recommendations, cyber security practices, security vulnerabilities and mitigation techniques, and other measures that could improve their security posture.
- Collaboration and Reporting: Collaborating with other IT and security professionals to enhance security measures. Preparing reports for management that outline the current security status, incidents, and ongoing risks. Ensuring that your organization adheres to the laws, regulations, and standards related to information security.
Now that I’ve discussed your responsibilities, what are some of the skills you need to get there?
What Skills Do You Need to Be a Cyber Security Specialist?
Before you qualify as a specialist, soft skills are the most basic skill to possess in any tech job:
This really is a no-brainer. As with any tech job, communication, technical writing, problem-solving, attention to detail, the ability to work under pressure, a positive attitude, teamwork, and a good work ethic are always expected.
According Cyberseek, the top skills for a specialist range from information security/assurance to internal auditing.
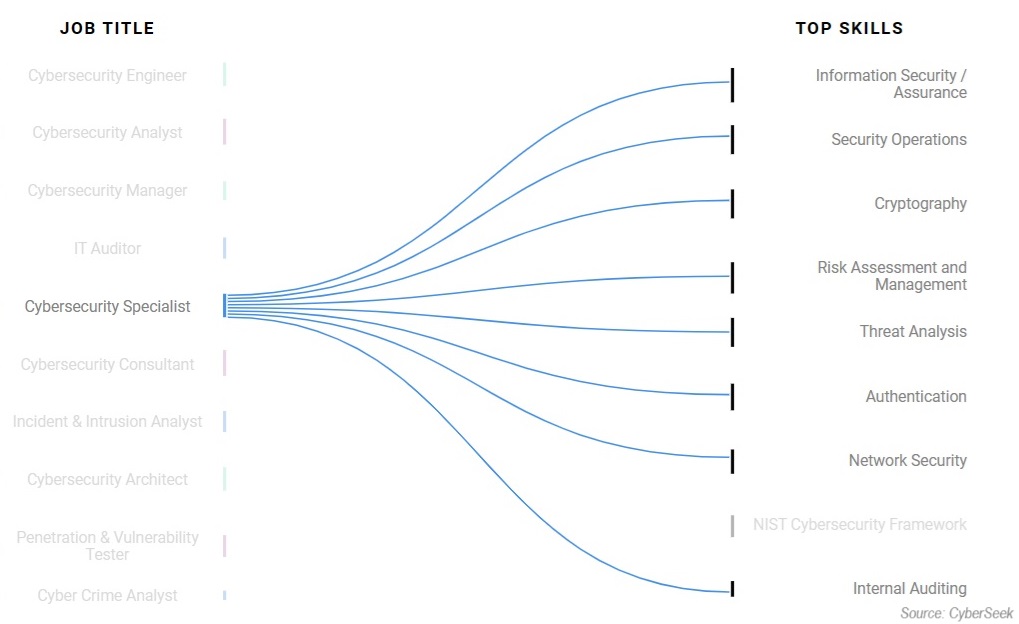
That’s obviously not surprising considering all the duties I just discussed. But this doesn’t seem very helpful. I mean at that point, you might as well know everything except for the NIST Cybersecurity Framework!
Here’s another attempt by Spiceworks to better identify your responsibilities.
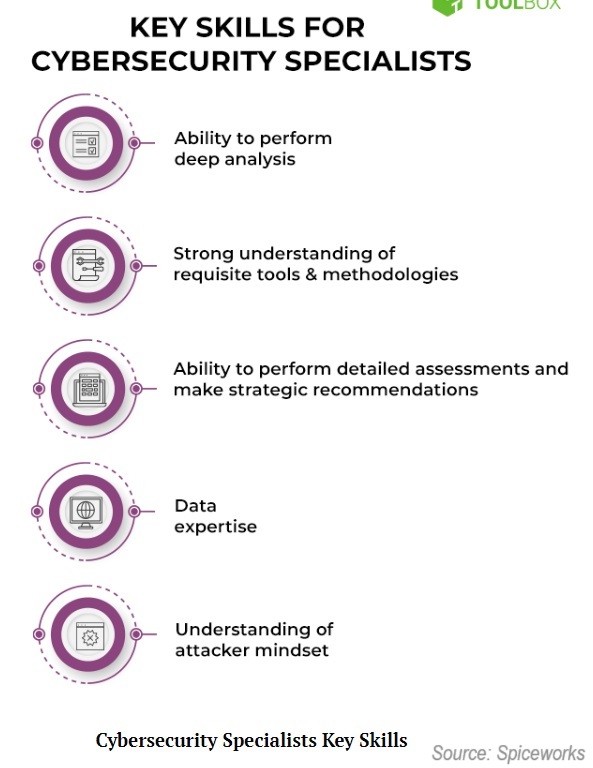
Nothing against the image, but the problem is…this looks like the skills of a cyber security analyst. I’ll talk about those differences later.
However, here’s what NICCS has mentioned which is a bit more granular:
- Applying host/network access controls (e.g., access control list)
- Tuning sensors
- Using incident handling methodologies
- Using Virtual Private Network (VPN) devices and encryption
- Securing network communications
- Protecting a network against malware (e.g., NIPS, anti-malware, restrict/prevent external devices, spam filters)
- System, network, and OS hardening techniques (e.g., remove unnecessary services, password policies, network segmentation, enable logging, least privilege, etc.)
- Troubleshooting and diagnosing cyber defense infrastructure anomalies
Now, what do you need to know to obtain those key skills?
What Knowledge Do You Need to Be a Cyber Security Specialist?
According to NICCS, the “core” cyber security specialist qualifications or knowledge areas for a cyber defense infrastructure support specialist are:
- computer networking concepts and protocols, and network security methodologies
- risk management processes (e.g., methods for assessing and mitigating risk)
- laws, regulations, policies, and ethics as they relate to cybersecurity and privacy
- cyber security and privacy principles
- cyber threats and vulnerabilities and the operational impacts of cyber security lapses
- host/network access control mechanisms (e.g., access control list, capabilities lists)
- incident response and handling methodologies
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) security
- what constitutes a network attack and a network attack’s relationship to both threats and vulnerabilities
- cyber defense and information security policies, procedures, and regulations
- network security architecture concepts including topology, protocols, components, and principles (e.g., application of defense-in-depth)
- test procedures, principles, and methodologies (e.g., Capabilities and Maturity Model Integration (CMMI))
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) tools and applications
- network protocols such as TCP/IP, Dynamic Host Configuration, Domain Name System (DNS), and directory services
- network traffic analysis (tools, methodologies, processes)
And how do you gain this knowledge?
Do You Need a Degree for Cyber Security Specialist?
The education requirements for cyber security specialist are quite easy. And you don’t need a cyber security degree to become a security specialist.
Instead, you’ll do much better with certifications.
Cyber Security Specialist Certifications
Before you start with other certifications, it’s a good idea to get your CompTIA Security+ certification first.
Once you’ve got that under your belt, there are several other options to choose from specific to cyber security specialists (none of which I’m getting paid for).
College Certificate Programs
I’m starting to see several colleges and universities offer Cyber Security Specialist Certificate programs. For example Southwestern Illinois College offers a program to help you prepare to take the CompTIA Security+ and Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certifications.
After you successfully complete the program, you’re supposed to qualify for:
- Information Security Analyst
- Firewall Specialist
- Network Security Specialist
- Security Administrator
- VPN Specialist
- Data Assurance Specialist
In general, college certificate programs give you classroom instruction and are a far cheaper option than enrolling in a cyber security bootcamp, or getting a degree. For most, the program can be completed in 1-2 semesters at your local community college and costs between $2,000 – $4,000 (educationdata.org).
Coursera
Coursera offers the, “IBM and ISC2 Cybersecurity Specialist Professional Certificate” which as you guessed is a joint program between IBM and ISC2.

It combines elements of ISC2’s Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) certification with the IBM Cybersecurity Specialist Professional Certificate, but don’t bother looking on ISC2’s website, you won’t find much else about it.
According to Coursera, it’s a popular, and comprehensive, certificate program with 6,600+ students designed to get you ready in less than four months, and with no prior experience needed. Here’s what the program offers:
- Core Skills Learned: Cryptography, network security, security risk assessment, and intrusion detection.
- Practical Training: You’ll learn to assess and secure computer systems, identify vulnerabilities, and implement cybersecurity solutions.
- Certification: After completion, you’ll earn a professional certificate from IBM, an IBM Digital Badge, and have free access to ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity exam for a limited time.
- Applied Learning Project: Your hands-on projects include installing security software, network troubleshooting, managing device settings, and developing security plans in a capstone project.
The great thing about Coursera is the cost. It runs $49 per month which is much cheaper than the college certificate program. Now, this is great if you’re okay to learn online, but not so much if you prefer in-person learning.
Cyber Security Certifications
The final option I’ll mention are your more traditional certifications. There are three certifications I was able to find:
EC-Council Certified Security Specialist (ECSS)
This certification starts with a 5-day course after which you’ll take the 100-question, 3-hour exam, online. For this exam, 70% is considered passing. Do your research for this certification as I’ve read mixed reviews regarding the benefits of EC-Council certifications.
GIAC Experienced Cybersecurity Specialist Certification (GX-CS)
Offered by SANS, this certification isn’t your typical exam format. It’s an open book, open note 4-hour exam that asks 25 “CyberLive” hands-on, real-world practical questions. It simulates a lab environment where you prove your skills using programs, code, and virtual machines.
DOD Security Specialist GS101.01
This course is reserved for government employees and contractors. If that’s you, you’re lucky because it’s probably free for you. This is a 7-day course with an exam at the end requiring 75% to pass.
How Long Does It Take to Be a Cyber Security Specialist?
On average expect to have a minimum of 3 to 5 years of experience in your specialization before you can be considered a specialist. But the actual years of experience required will usually depend on the role they’ll want you to take on.
Cyberseek shows this as an entry level role, compared to a cyber security analyst position.
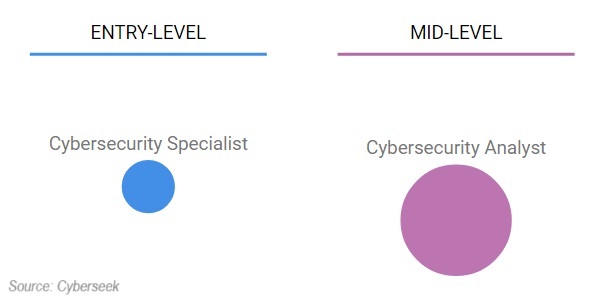
However, I’m not convinced this is completely accurate.
NICCS shows a list of feeder roles that are likely to give you a better shot of becoming a cyber security specialist.
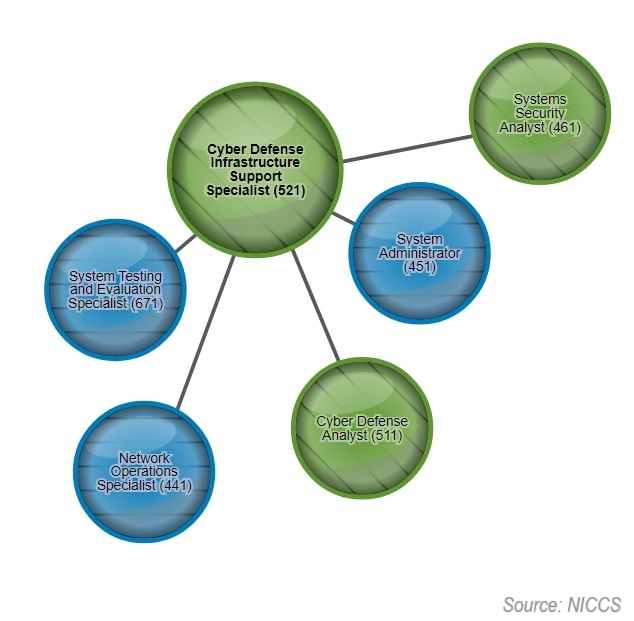
Along with a list of job titles that have some amount of overlap with a specialist.
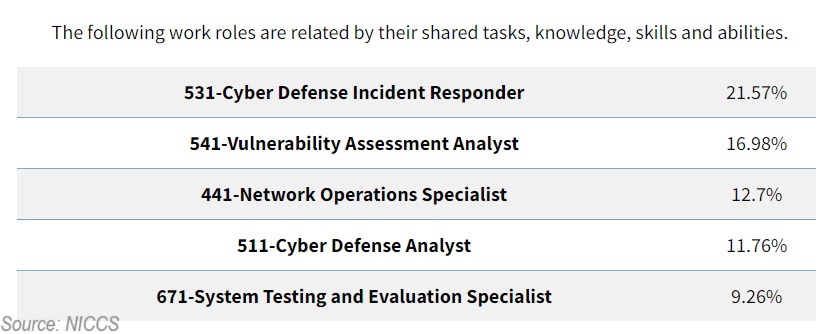
If you have 30%-40% of the shared responsibilities indicated above, you’ve got a pretty good chance at finding a cyber security specialist job.
Cyber Security Specialist vs Analyst?
While both cyber security analyst and specialist have some overlapping responsibilities, they are different in scope and expertise:
Cyber Security Analyst
- Typically considered an entry to mid-level role.
- Focuses mainly on monitoring, detecting, and responding to security incidents.
- Involves analyzing data and security alerts, identifying vulnerabilities, and often contributing to the incident response process.
- Analysts may also participate in maintaining security tools and contributing to policy development.
- Example of responsibilities: monitoring systems for security breaches, investigating security incidents, and analyzing security data to identify and mitigate risks. They often use tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems to collect and analyze security logs, as well as threat intelligence platforms to stay updated on emerging threats.
Cyber Security Specialist
- Can be seen as a mid-level to senior role, depending on the organization and the specific responsibilities.
- Often has a broader scope of responsibilities, which might include designing, implementing, and managing security solutions across the organization.
- Specialists may take on more complex projects and strategic planning in addition to the operational tasks of an analyst.
- This role typically requires deeper technical expertise and may specialize in areas such as network security, application security, or endpoint security.
- Example of responsibilities: configuring firewalls, implementing encryption protocols, conducting security audits, and responding to security incidents.
The distinction between an analyst and a specialist can sometimes be fluid and largely depends on the organization’s structure and the specific job descriptions.
Some organizations might use these titles interchangeably, while others distinguish between them based on the complexity of the responsibilities, the level of autonomy, or the focus of the role.
Generally, a specialist is thought to have a broader or deeper level of expertise compared to an analyst, who primarily focuses on operational and monitoring tasks.
TL;DR
In this article, I delve into the world of cyber security specialists, offering insights and guidance for those interested in pursuing this career path. I start by clarifying the role, emphasizing its importance in protecting organizations from cyber threats. From risk assessment to incident response, cyber security specialists play a vital role in ensuring the integrity of computer systems and networks.
Next, I address the crucial topic of salary, highlighting the lucrative opportunities available in the field, with entry-level salaries averaging around $83,834 annually. The demand for cyber security specialists is also discussed, with thousands of job openings nationwide, indicating strong job stability and growth prospects.
Moving on, I explore the educational and certification requirements for aspiring cyber security specialists. While a degree is not mandatory, certifications such as CompTIA Security+ are highly recommended. Additionally, I outline the essential skills and knowledge areas needed for success in this role, covering everything from threat identification to compliance and auditing.
Finally, I differentiate between cyber security analysts and specialists, clarifying the distinct responsibilities and expertise required for each role.
Looking for a Cyber Security Specialist Job?
View our listing of cybersecurity jobs!
Final Thoughts
Are you ready to become a cyber security specialist?
If you’re already a specialist, how did you become one?
Tell me what you think in the comments below!



